Stronger networks make stronger communities
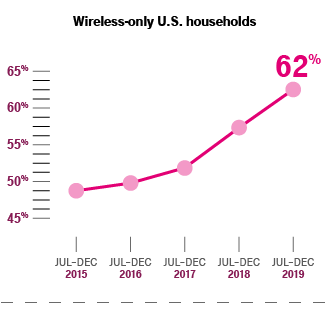
Every day America becomes more dependent on wireless
Not so long ago, making a voice call from anywhere was novel. Now hundreds of millions of Americans use their mobile devices to browse the internet, use social media, and stream feature length films—simultaneously.
With an ever-increasing demand for fast and reliable wireless service, infrastructure must be built and upgraded all the time.
With 100x greater capacity than 4G LTE, the 5G revolution is here. It is going to change the way we live, and it all hinges on nationwide network coverage and capacity.
What is 5G?
What is 5G technology? It is like the ultimate speed and connectivity without boundaries.
Coverage and capacity
Cell coverage is more than just a map of the U.S. with a brand-color overlay. Network performance requires constant optimization.
COVERAGE

CAPACITY

Without fast, reliable cell coverage, my small business is dead in the water. Knowing our phones will work all the time is crucial to our success.
How a strong network is built
Our site selection process is more than thorough, it's exhaustive. These are just a few factors we consider before determining the best place to install a cell site.


STANDARDS
REQUIREMENTS
USAGE NEEDS

MAN-MADE OBSTACLES

LOCATIONS