
Anatomy of a strong network
How mobile works. Literally.
Wireless communications requires more infrastructure than many people realize. It takes a network with millions of components working in-concert to transmit data from one device to another.

An overview of T-Mobile network infrastructure that connects wireless customers around the globe.
A holistic view of network infrastructure
A lot happens between “sending…” and “got it!” Whether it’s a text, a call, a web search or a streaming video—all wireless data travels along similar paths. The typical path a signal takes looks something like the simplified diagram below.
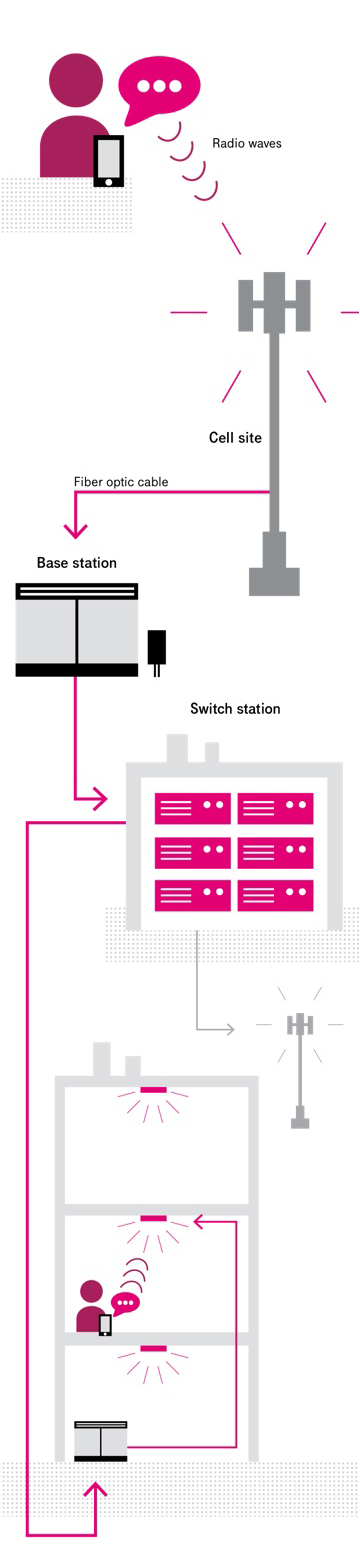
Why network updates never stop
Much like roads or highways, networks must be continuously upgraded to support ever-increasing wireless traffic. Often, this means installing more antennas in more places, as well as making sure there’s a high-speed connection back to the core network.
Types of antennas (cell sites)
When it comes to antennas or cell sites, one size does not fit all needs. Wireless network science has come a long way, and there are now multiple kinds of technologies that can be deployed—each with unique purposes and challenges.
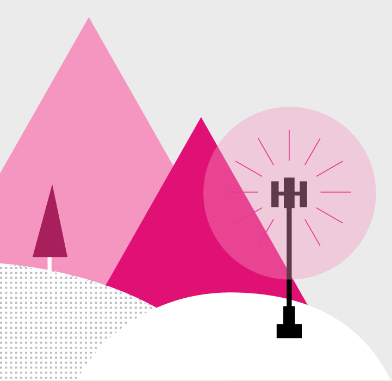
MACRO SITES
What many people think of when they hear “cell site.” These range from 50’ – 200’ high and cover an area of one-half mile to several miles.
SMALL CELLS
Low-powered and compact, these cells sites cover a smaller area. They provide extra capacity for high-traffic areas and are also used for indoor coverage.Wireless network performance
Performance depends on both coverage and capacity. When a cell site is overloaded with demand, webpages won’t load quickly, video or text messages are slow to send, and phone calls may be dropped or not get through at all.
To provide customers with the mobile experience they expect, our team monitors cell sites with high data usage and, when necessary, we add more antennas and radios. Other times, our radio wave experts direct us to build a network more densely populated with additional frequencies, cell sites or small cells.
Small cells and densification: More people and more data on our network means having more cell sites closer to the customers who use them. Watch to learn more.
Why we need a denser network of cell sites
A technological revolution built on our 4G LTE foundation—connecting trillions of devices like autonomous cars, smart homes, and entire smart cities in the Internet of Things (IoT).
Network telecommunications standards
 Was capable of digital phone calls, text messaging and basic data services.
Was capable of digital phone calls, text messaging and basic data services.
 Introduced integrated voice, messaging, mobile internet, broadband data and apps.
Introduced integrated voice, messaging, mobile internet, broadband data and apps.
 Enabled high-speed internet, high-capacity multimedia, and more reliable connections. Mobile ridesharing services did not exist before this generation of wireless.
Enabled high-speed internet, high-capacity multimedia, and more reliable connections. Mobile ridesharing services did not exist before this generation of wireless.

A technological revolution built on our 4G LTE foundation—connecting trillions of devices like autonomous cars, smart homes, and entire smart cities in the Internet of Things (IoT).
How a site is selected
When it comes to selecting a location for a cell site, our process is exhaustive.






Whenever possible, cell sites are built on existing infrastructure, buildings, and rooftops. Our siting experts work to install antennas that will work at an optimal level while blending in with the surrounding environment.


